What is ultrasonic metal welding?
1. Vibration generation
The beginning of the ultrasonic welding process is generated by the ultrasound transducer. This transducer is usually made of piezoelectric ceramic material and generates mechanical vibration when an electric field is applied. Such vibrations are usually located in the high frequency range from 15 kHz to 40 kHz, which is the frequency range of ultrasound waves.

2. Focusing energy
These high frequency vibrations are transmitted through the transducer to the welding horn, focusing the energy at the material to be fused. This focusing energy is a key feature of ultrasonic welding, which enables a high degree of mechanical stress in the fusion region.
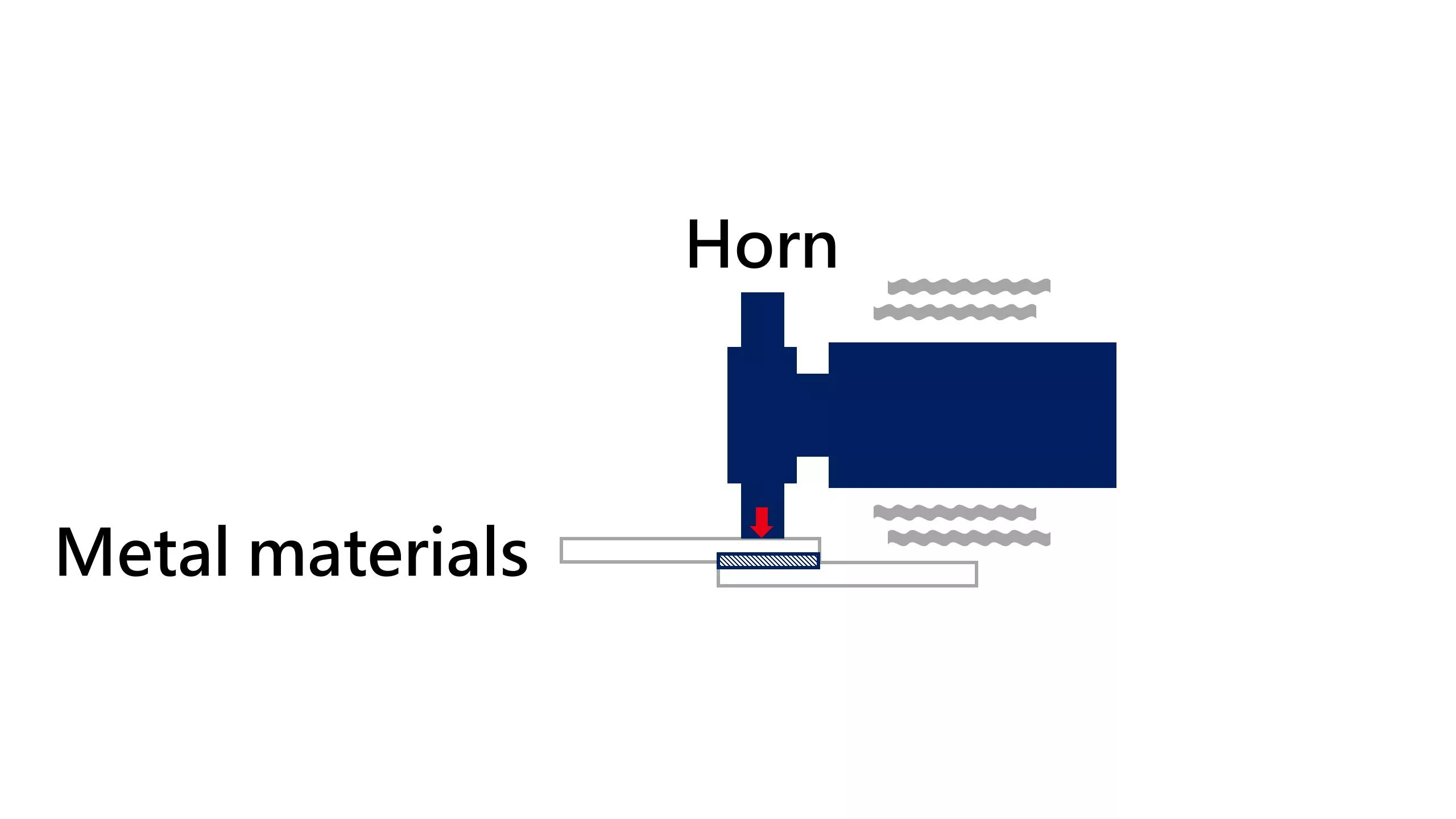
3. Material fusion
Due to high mechanical stress, the binding between material molecules is disrupted and a plastic deformation forms on the surface of the fused region. This allows two or more materials to be fused to each other, form a robust fusion bond. Ultrasonic vibrations caused this plastic deformation without requiring an additional heating source.
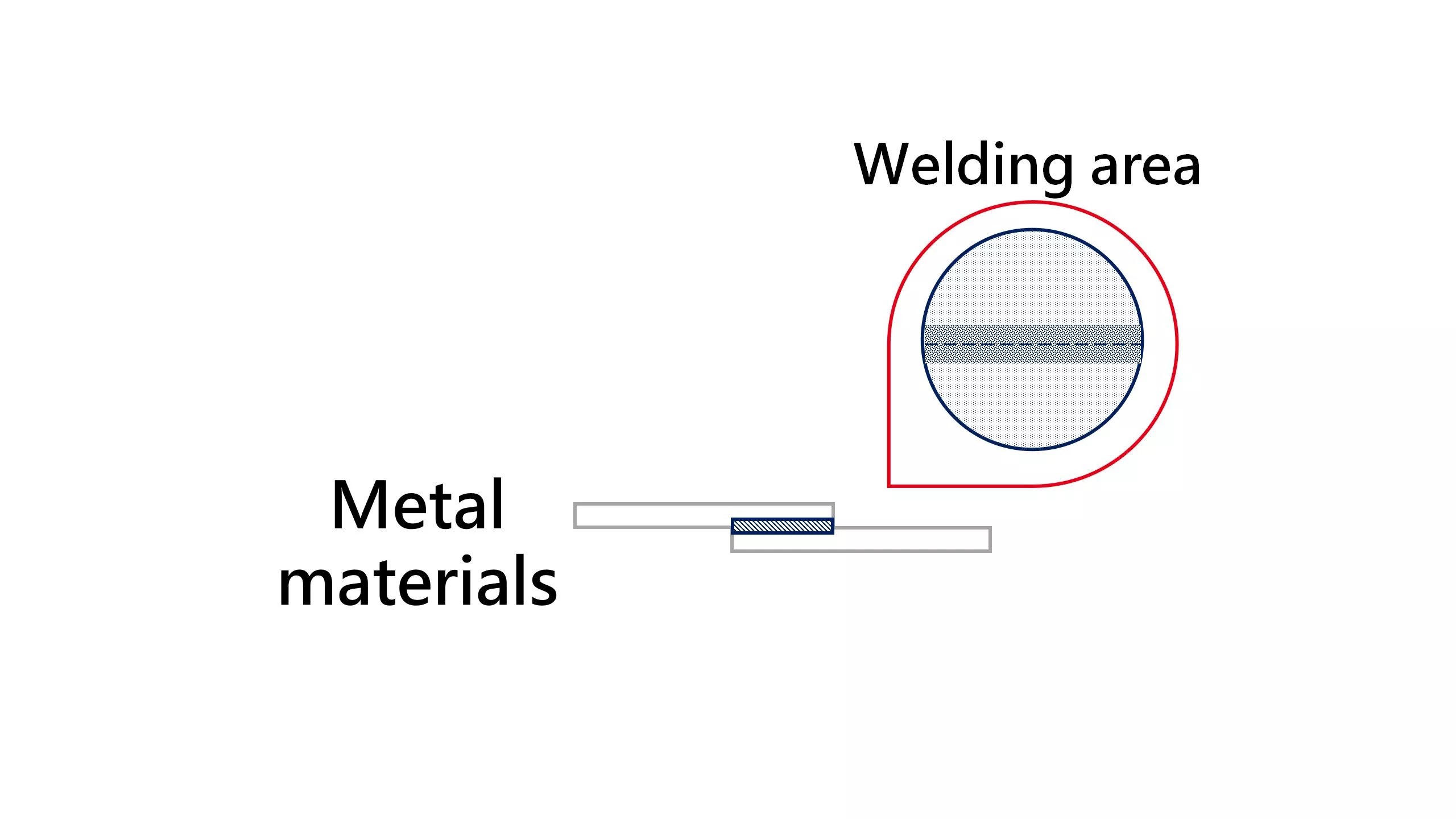
The principle of ultrasonic wave bonding makes it applicable to a variety of materials, including plastics, metal and textiles. However, the parameters of the fusion process, such as amplitude, pressure, and time, must be adjusted according to the materials.